Microfabricated chip for X-ray medical images technology
(Cet article n'est disponible qu'en anglais)
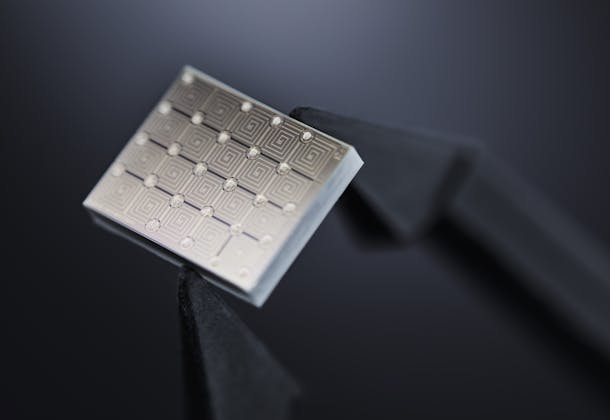
X-rays are produced when accelerated electrons hit a positively biased target. For over a hundred years, the electron beam in X-ray tubes has been produced by heating a tungsten filament to over 2000°C (hence the “Hot Cathode” X-ray tube). This is now about to change: the tech company Nanox Imaging Ltd is developing a multi-source Digital Tomosynthesis system where the electron stream is generated by a field-emission chip (Hence a “Cold Cathode” tube). Tomosynthesis enhances anatomy visualization with multiple layers and reduces the super-imposition of structures. The chip containing the field emitter array for the new system is microfabricated at CSEM’s specialized MEMS foundry services, among others.