January 14, 2022
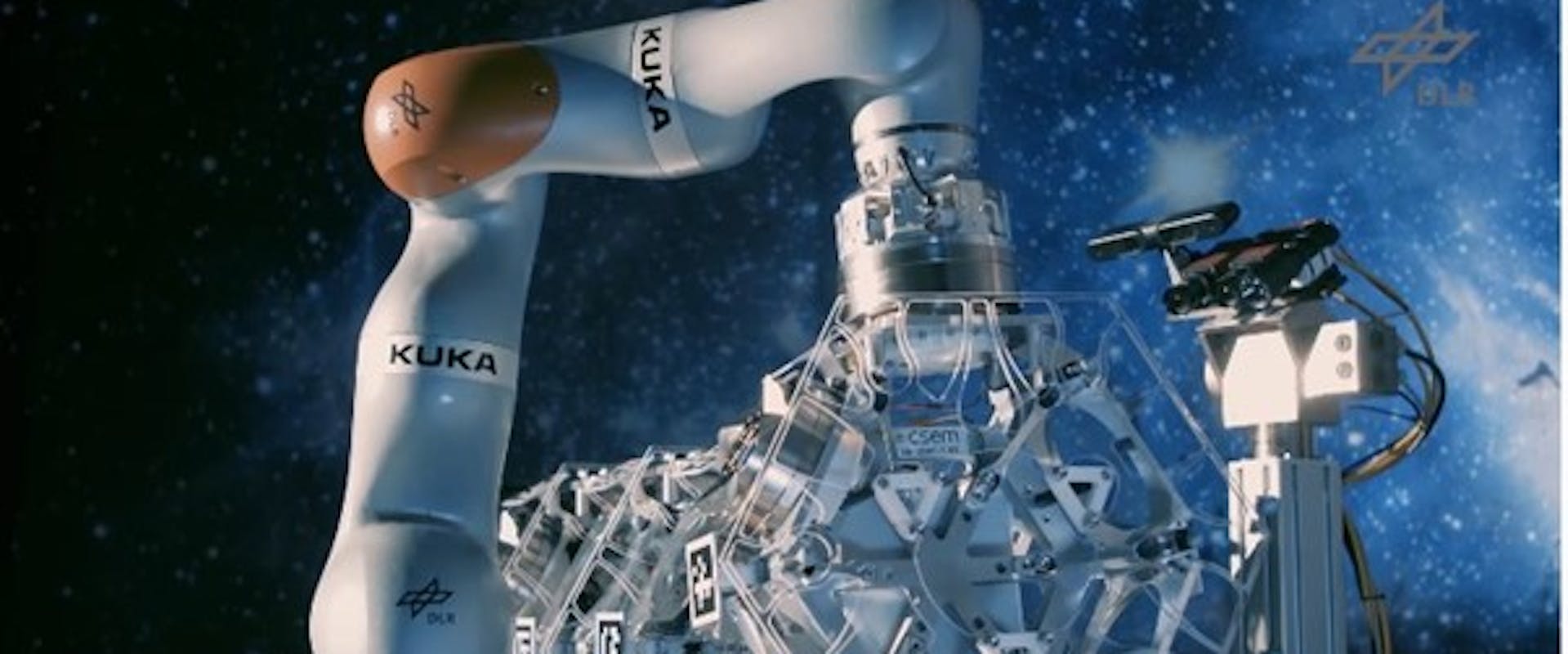
Autonomous robots will one day assemble telescopes directly in space
Engineers working under the EU-funded project PULSAR, have unveiled a fully autonomous robotic demonstrator, which could construct in orbit the primary mirror of a telescope from separate parts. The system, which includes components developed by CSEM, paves the way towards the assembly of giant telescopes directly in space – telescopes that would otherwise be too big to launch into orbit in a single piece. What’s more, the autonomous system has the potential in the future to construct other large space structures, such as orbiting solar panels or solar sails.